Over the past decade there has been a growing concern over the presence of polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in drinking water. PFAS are a new class of man-made emerging contaminants, that include PFOA and PFOS. They are emerging in nature because they are the substances that are not commonly regulated in the environment and having known or suspected to have deleterious effects on humans and the ecosystem. According to the research from Harvard University, more than 16 million Americans drink water contaminated with toxic chemicals that can be traced to military and industrial sites but PFOA affect people worldwide, or perhaps even India.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) includes PFOA (Perfluorooctanoic Acid), PFOS (Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid), GenX, and many other chemicals. PFOA and PFOS have been the most extensively produced and studied of these chemicals.
One of the leading company which used perfluorooctanyl sulfonate (PFOS) in the manufacturing process, voluntarily phased out the same and found substitutes for the chemistry. The company reformulated its production process. However, between 2001 and 2005, there was growing evidence that PFAS had migrated into surface and groundwater, contaminating potable water supplies around manufacturing plants.
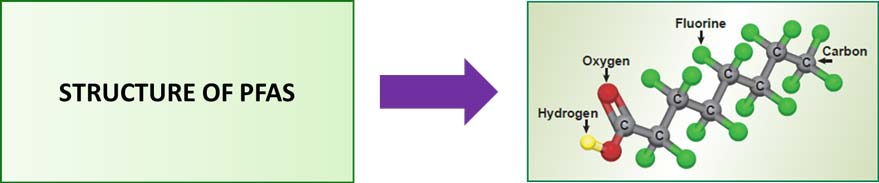
PFAS and PFOS are very persistent in the environment and in the human body, because their structure is composed of extensive carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds and C-F bond which is known to be extremely strong and stable. Due to very strong and stable C-F bonds, typical environmental and metabolic degradation of PFAS is extremely slow (half-life over 5 years) and over a time they bio-accumulate inside the body and can interfere with endogenous metabolic processes.
Excessive exposure to PFAS, may cause high cholesterol, increased liver enzymes, decreased vaccination response, thyroid disorders, pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia, and cancer.
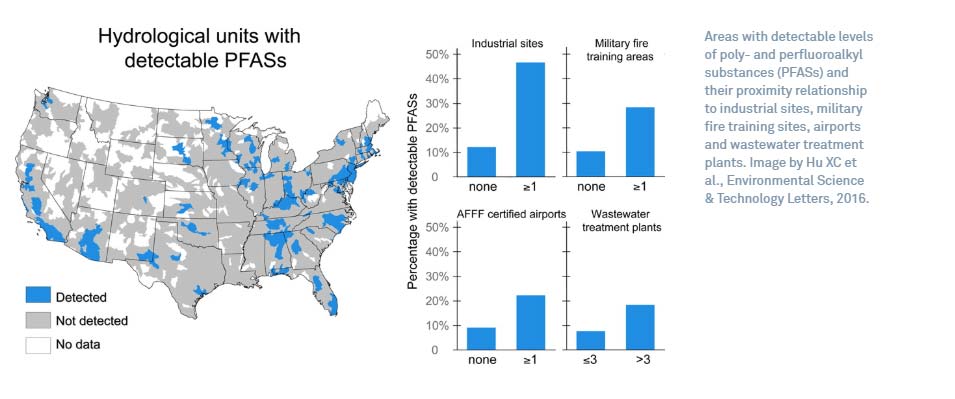
Between 2013 and 2015, 36,000 drinking water samples from 4,864 public water sources were collected by the EPA. They found PFAS in water systems that serve more than 33 states, three American territories and the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community. California had the highest frequency of detection, followed by New Jersey, North Carolina, Alabama, Pennsylvania, Ohio, New York, Georgia, Minnesota, Arizona, Massachusetts, and Illinois.
According to the treatment done in 2016 on Public water systems, private drinking wells and military water supplies, EPA advised people not to drink water if it had more than 70 parts per trillion (ppt) of PFOA and PFOS chemicals, a level that some researchers said was inadequate to protect public health.
The HHS agency said the level should be 7-ppt for PFOS and 11-ppt for PFOA — the two common PFAS compounds.
WHERE IS PFAS FOUND?
PFAS can be found in air, water and soil. These substances break down into the air, falls to the soil and eventually enter water bodies.
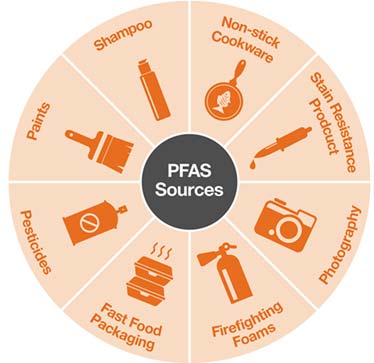
Other areas where PFAS is found are:
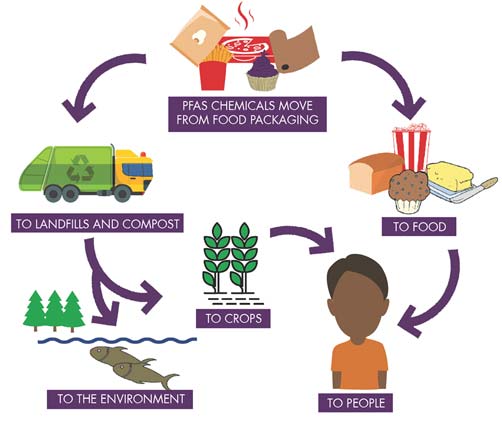
- Food wrappers containing PFAS material processed with equipment that uses PFAS.
- Commercial household products, including stain and water-repellent fabrics, non-stick products, polishes, waxes, paints, cleaning products, and fire-fighting foam is also a major source of groundwater contamination at airports and military bases where firefighting training occurs.
- Workplace, including production facilities or industries that use PFAS.
- Drinking water, typically localized and associated with a specific facility like, manufacturer, landfill, wastewater treatment plant, firefighter training facility.
- Living organisms, including fish, animals and humans, where PFAS can build up and persist over time.
YOU CAN’T BOIL WATER WITH PFAS

The best way to reduce the effect of PFAS in water is through filtration:
Catalytic activated carbon / carbon blocks is an emerging technique in water filtration industry which proves to be an effective treatment for PFAS removal. The reason behind this stands to be its effective adsorbent capability, highly porous nature and large surface area. Activated carbon will adsorb natural organic compounds, taste and odor, synthetic organic chemicals in drinking water treatment systems. In the manufactiuring process of Catalytic Carbon, the physical and chemical adsorbtion property is enhanced thereby improving the peformance.
This method can be 100% effective for a time period depending on the type of carbon used, depth of bed carbon, water flow rate, specific PFAS that needs to be removed, temperature, type of organic matter, other contaminants that are present in the water.
Filtrex Technologies manufactures carbon blocks and catalytic carbon that can be used in the reduction of PFAS and other harmful chemicals through the method of filtration at the POE and POU level. All our blocks have been tested and certified by global agencies like NSF and WQA and we pass all the water quality standards.




