Microplastics are small, barely visible pieces of plastic that enter and pollute the environment. These are not specific kind of plastic, but rather any type of plastic fragments that are less than 5 millimeters in length. Microplastics are the sad result of the use of plastics that has taken the world since its invention. They enter natural ecosystems from a variety of sources like cosmetics, clothing, and industrial processes.
Microplastics are classified in two ways:


According to
“The World Health Organisation (WHO) has launched a
In the new study, analysis of 259 bottles from 19 locations in nine countries across 11 different brands found an average of 325 plastic particles for every
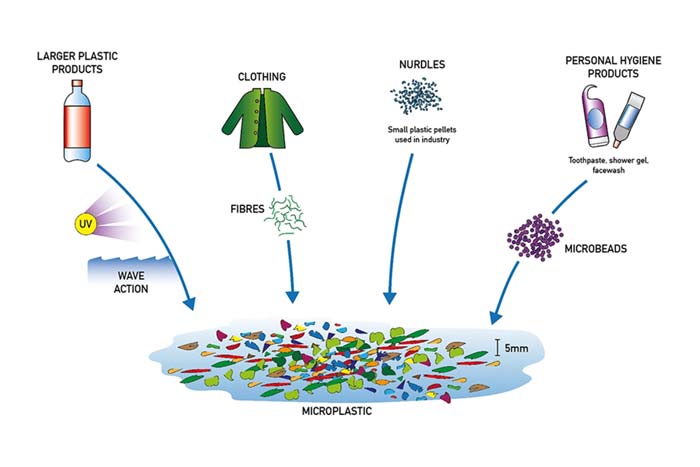
SOURCES OF MICROPLASTIC
Environmental Action
Plastics do not decompose, but they are broken down. As the plastic waste and debris floats around the ocean, they are exposed to solar radiation and constant abrasion from the action of wind and water waves. Over time, these elements break down the plastics into smaller chunks of debris and the cycle continues until they become microscopic.
Human cosmetics
While environmental action is the most common way for formation of microplastics, other relevant means comes from intentional human production of small beaded plastics. These are found in skin care and hygiene industry where small, plastic, microbeads are added to products such as shower gels and facial scrubs to increase their qualities for proper exfoliation and cleaning. These microbeads then slowly find their way into the water systems.
Clothing
Other source of microplastics come in the form of microfibres. When human clothing is washed plastic sheds into the water in shape of microscopic fibres. These are arguably worse than the relatively spherical microplastics because they have a larger surface area.
TOXICOLOGY AND RISK FACTOR
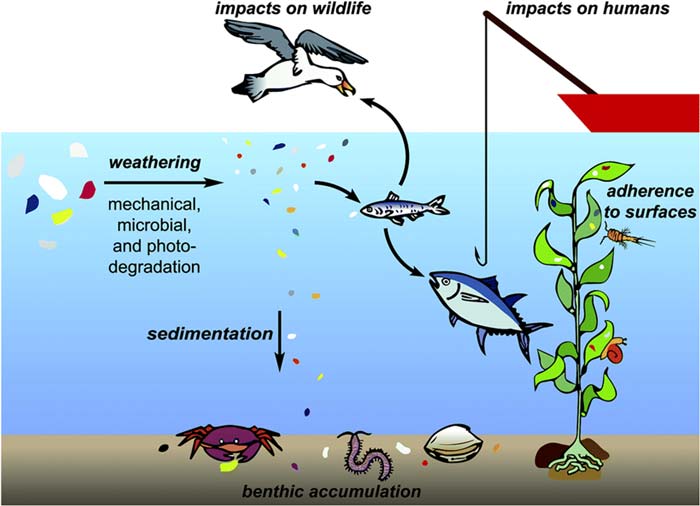
Environmental Risk:
Accumulate in water and reside there for a long time. Toxins present in microplastic bio-accumulate. Leach contaminants that can cause cancer. Potential to accumulate in human body who consumed marine organism. Small microplastic serves to transport various other contaminants e.g. persistent organic pollutant (POPs) and bring them inside human body.
Chemical Risk:
When exposed to UV rays, releases harmful chemicals, many of them are unknown or may not be found in nature. Has adverse effect on fetal development and hormone levels. Cancer causing entity. High surface area may cause toxic elements to get attached/adsorbed and being transported into human bodies.
FACT:
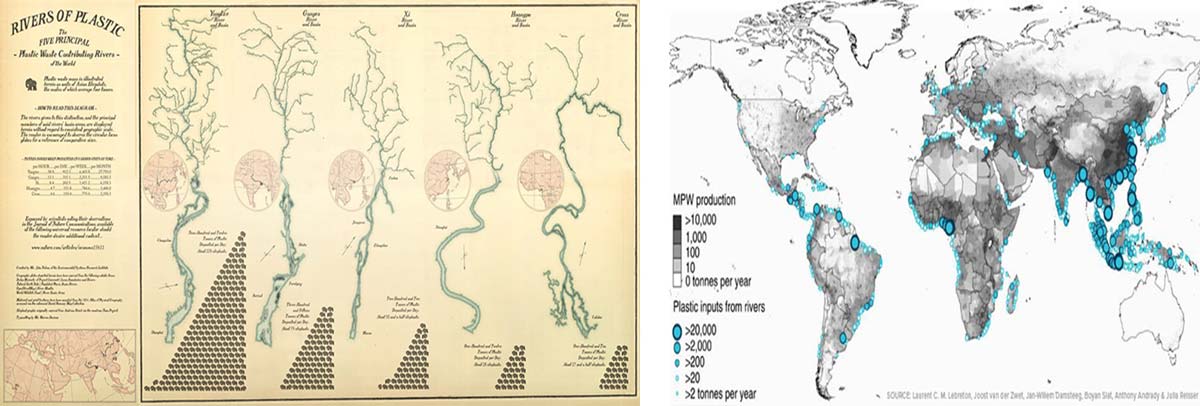
Every year, approximately eight million metric tons of plastic enters the world’s oceans and only 10% of it ends up being recycled, and the rest congregates in places like the Pacific Garbage Patch contaminating the water bodies. Latter these waters enter our houses through various ways which poses a serious threat to human life’s if not treated well. The treatment process can be carried out carried out either at the point-of-entry of point- of-use stage and by using various kinds of water filtration products.
Filtrex Technologies manufactures Compression Moulded Carbon Blocks that can remove microplastics. The micron rating of our blocks varies from 0.1-40micron.
Even if the blocks are assembled with Non-RO, Non-UV water purification devices, i.e. as a
For more information about our products, visit our websites:
